package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableLoadTimeWeaving.AspectJWeaving;
import org.springframework.context.weaving.AspectJWeavingEnabler;
import org.springframework.context.weaving.DefaultContextLoadTimeWeaver;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAttributes;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import org.springframework.instrument.classloading.LoadTimeWeaver;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
* {@code @Configuration} class that registers a {@link LoadTimeWeaver} bean.
* <p>This configuration class is automatically imported when using the
* {@link EnableLoadTimeWeaving} annotation. See {@code @EnableLoadTimeWeaving}
* javadoc for complete usage details.
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see LoadTimeWeavingConfigurer
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME
@Configuration
public class LoadTimeWeavingConfiguration implements ImportAware, BeanClassLoaderAware {
@Nullable
private AnnotationAttributes enableLTW;
@Nullable
private LoadTimeWeavingConfigurer ltwConfigurer;
@Nullable
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
@Override
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {
this.enableLTW = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importMetadata, EnableLoadTimeWeaving.class);
if (this.enableLTW == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"@EnableLoadTimeWeaving is not present on importing class " + importMetadata.getClassName());
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setLoadTimeWeavingConfigurer(LoadTimeWeavingConfigurer ltwConfigurer) {
this.ltwConfigurer = ltwConfigurer;
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
@Bean(name = ConfigurableApplicationContext.LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public LoadTimeWeaver loadTimeWeaver
() {
Assert.state(this.beanClassLoader != null, "No ClassLoader set");
LoadTimeWeaver loadTimeWeaver = null;
if (this.ltwConfigurer != null) {
loadTimeWeaver = this.ltwConfigurer.getLoadTimeWeaver();
if (loadTimeWeaver == null) {
loadTimeWeaver = new DefaultContextLoadTimeWeaver(this.beanClassLoader);
if (this.enableLTW != null) {
AspectJWeaving aspectJWeaving = this.enableLTW.getEnum("aspectjWeaving");
switch (aspectJWeaving) {
case DISABLED:
break;
case AUTODETECT:
if (this.beanClassLoader.getResource(AspectJWeavingEnabler.ASPECTJ_AOP_XML_RESOURCE) == null) {
break;
AspectJWeavingEnabler.enableAspectJWeaving(loadTimeWeaver, this.beanClassLoader);
break;
case ENABLED:
AspectJWeavingEnabler.enableAspectJWeaving(loadTimeWeaver, this.beanClassLoader);
break;
return loadTimeWeaver;
LoadTimeWeavingConfiguration首先在setImportMetadata读取EnableLoadTimeWeaving注解信息,然后注册一个名称为loadTimeWeaver类型为LoadTimeWeaver的Bean(注册虽然在后面注入自定义LoadTimeWeaver方法之前,但是真实回调构造对象却是在自动注入属性之后的,所以以上的方式没啥问题)。如果ltwConfigurer(用户自定义的LoadTimeWeaver,通过自动注入的方式)为空,则默认值为DefaultContextLoadTimeWeaver。注解信息不为空,则根据注解信息通过AspectJWeavingEnabler.enableAspectJWeaving开启功能。
org.springframework.context.weaving.AspectJWeavingEnabler#enableAspectJWeaving
* Enable AspectJ weaving with the given {@link LoadTimeWeaver}.
* @param weaverToUse the LoadTimeWeaver to apply to (or {@code null} for a default weaver)
* @param beanClassLoader the class loader to create a default weaver for (if necessary)
public static void enableAspectJWeaving(
@Nullable LoadTimeWeaver weaverToUse, @Nullable ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
if (weaverToUse == null) {
if (InstrumentationLoadTimeWeaver.isInstrumentationAvailable()) {
weaverToUse = new InstrumentationLoadTimeWeaver(beanClassLoader);
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("No LoadTimeWeaver available");
1. weaverToUse = new DefaultContextLoadTimeWeaver(this.beanClassLoader);
weaverToUse.addTransformer(
new AspectJClassBypassingClassFileTransformer(new ClassPreProcessorAgentAdapter()));
在执行以上方法之前还要考虑AspectJWeavingEnabler类在Spring中是否是一个需要额外处理的类。
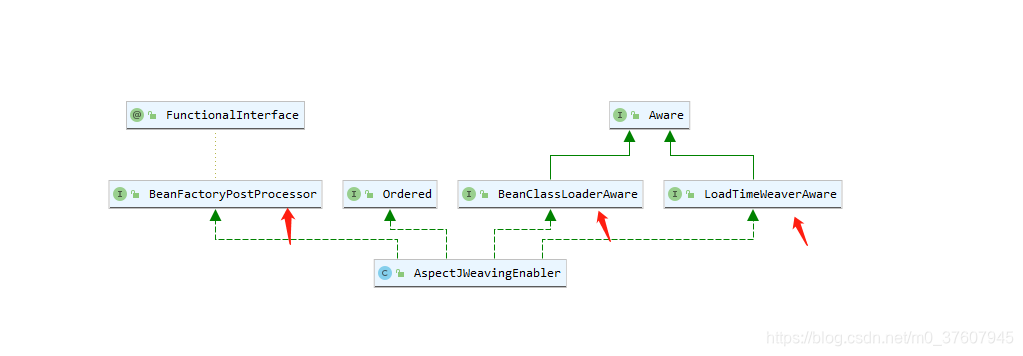
首先需要执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的逻辑,然后是在这个类实例化的时候,执行BeanClassLoaderAware和LoadTimeWeaverAware方法。但没又发现其他地方会注册这个Bean(整个过程是通过EnableLoadTimeWeaving开启的,在这里面没有响应注册AspectJWeavingEnabler的逻辑)。
* ClassFileTransformer decorator that suppresses processing of AspectJ
* classes in order to avoid potential LinkageErrors.
* @see org.springframework.context.annotation.LoadTimeWeavingConfiguration
private static class AspectJClassBypassingClassFileTransformer implements ClassFileTransformer {
private final ClassFileTransformer delegate;
public AspectJClassBypassingClassFileTransformer(ClassFileTransformer delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
@Override
public byte[] transform(ClassLoader loader, String className, Class<?> classBeingRedefined,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain, byte[] classfileBuffer) throws IllegalClassFormatException {
if (className.startsWith("org.aspectj") || className.startsWith("org/aspectj")) {
return classfileBuffer;
return this.delegate.transform(loader, className, classBeingRedefined, protectionDomain, classfileBuffer);
对应真正干活的delegate是org.aspectj.weaver.loadtime.ClassPreProcessorAgentAdapter
package org.aspectj.weaver.loadtime;
import java.lang.instrument.ClassFileTransformer;
import java.lang.instrument.IllegalClassFormatException;
import java.security.ProtectionDomain;
* Java 1.5 adapter for class pre processor
* @author <a href="mailto:alex@gnilux.com">Alexandre Vasseur</a>
public class ClassPreProcessorAgentAdapter implements ClassFileTransformer {
* Concrete preprocessor.
private static ClassPreProcessor s_preProcessor;
static {
try {
s_preProcessor = new Aj();
s_preProcessor.initialize();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("could not initialize JSR163 preprocessor due to: " + e.toString());
* Invokes the weaver to modify some set of input bytes.
* @param loader the defining class loader
* @param className the name of class being loaded
* @param classBeingRedefined is set when hotswap is being attempted
* @param protectionDomain the protection domain for the class being loaded
* @param bytes the incoming bytes (before weaving)
* @return the woven bytes
public byte[] transform(ClassLoader loader, String className, Class<?> classBeingRedefined, ProtectionDomain protectionDomain,
byte[] bytes) throws IllegalClassFormatException {
if (classBeingRedefined != null) {
System.err.println("INFO: (Enh120375): AspectJ attempting reweave of '" + className + "'");
return s_preProcessor.preProcess(className, bytes, loader, protectionDomain);
对应的接口
package org.aspectj.weaver.
loadtime;
import java.security.ProtectionDomain;
* Generic class pre processor interface that allows to separate the AspectJ 5 load time weaving from Java 5 JVMTI interfaces for
* further use on Java 1.3 / 1.4
* @author Alexandre Vasseur
public interface ClassPreProcessor {
* Post constructor initialization, usually empty
void initialize();
* Weave
* @param className
* @param bytes
* @param classLoader
* @param a protection domain that may be used for defining extraneous classes generated as part of modifying the one passed in
* @return
byte[] preProcess(String className, byte[] bytes, ClassLoader classLoader, ProtectionDomain protectionDomain);
它们之间的关系图如下所示
package java.lang.instrument;
import java.security.ProtectionDomain;
* An agent provides an implementation of this interface in order
* to transform class files.
* The transformation occurs before the class is defined by the JVM.
* Note the term <i>class file</i> is used as defined in section 3.1 of
* <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite>,
* to mean a sequence
* of bytes in class file format, whether or not they reside in a file.
* @see java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation
* @see java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#addTransformer
* @see java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#removeTransformer
* @since 1.5
public interface ClassFileTransformer {
* The implementation of this method may transform the supplied class file and
* return a new replacement class file.
* There are two kinds of transformers, determined by the <code>canRetransform</code>
* parameter of
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#addTransformer(ClassFileTransformer,boolean)}:
* <li><i>retransformation capable</i> transformers that were added with
* <code>canRetransform</code> as true
* </li>
* <li><i>retransformation incapable</i> transformers that were added with
* <code>canRetransform</code> as false or where added with
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#addTransformer(ClassFileTransformer)}
* </li>
* </ul>
* Once a transformer has been registered with
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#addTransformer(ClassFileTransformer,boolean)
* addTransformer},
* the transformer will be called for every new class definition and every class redefinition.
* Retransformation capable transformers will also be called on every class retransformation.
* The request for a new class definition is made with
* {@link java.lang.ClassLoader#defineClass ClassLoader.defineClass}
* or its native equivalents.
* The request for a class redefinition is made with
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#redefineClasses Instrumentation.redefineClasses}
* or its native equivalents.
* The request for a class retransformation is made with
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#retransformClasses Instrumentation.retransformClasses}
* or its native equivalents.
* The transformer is called during the processing of the request, before the class file bytes
* have been verified or applied.
* When there are multiple transformers, transformations are composed by chaining the
* <code>transform</code> calls.
* That is, the byte array returned by one call to <code>transform</code> becomes the input
* (via the <code>classfileBuffer</code> parameter) to the next call.
* Transformations are applied in the following order:
* <li>Retransformation incapable transformers
* </li>
* <li>Retransformation incapable native transformers
* </li>
* <li>Retransformation capable transformers
* </li>
* <li>Retransformation capable native transformers
* </li>
* </ul>
* For retransformations, the retransformation incapable transformers are not
* called, instead the result of the previous transformation is reused.
* In all other cases, this method is called.
* Within each of these groupings, transformers are called in the order registered.
* Native transformers are provided by the <code>ClassFileLoadHook</code> event
* in the Java Virtual Machine Tool Interface).
* The input (via the <code>classfileBuffer</code> parameter) to the first
* transformer is:
* <li>for new class definition,
* the bytes passed to <code>ClassLoader.defineClass</code>
* </li>
* <li>for class redefinition,
* <code>definitions.getDefinitionClassFile()</code> where
* <code>definitions</code> is the parameter to
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#redefineClasses
* Instrumentation.redefineClasses}
* </li>
* <li>for class retransformation,
* the bytes passed to the new class definition or, if redefined,
* the last redefinition, with all transformations made by retransformation
* incapable transformers reapplied automatically and unaltered;
* for details see
* {@link java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#retransformClasses
* Instrumentation.retransformClasses}
* </li>
* </ul>
* If the implementing method determines that no transformations are needed,
* it should return <code>null</code>.
* Otherwise, it should create a new <code>byte[]</code> array,
* copy the input <code>classfileBuffer</code> into it,
* along with all desired transformations, and return the new array.
* The input <code>classfileBuffer</code> must not be modified.
* In the retransform and redefine cases,
* the transformer must support the redefinition semantics:
* if a class that the transformer changed during initial definition is later
* retransformed or redefined, the
* transformer must insure that the second class output class file is a legal
* redefinition of the first output class file.
* If the transformer throws an exception (which it doesn't catch),
* subsequent transformers will still be called and the load, redefine
* or retransform will still be attempted.
* Thus, throwing an exception has the same effect as returning <code>null</code>.
* To prevent unexpected behavior when unchecked exceptions are generated
* in transformer code, a transformer can catch <code>Throwable</code>.
* If the transformer believes the <code>classFileBuffer</code> does not
* represent a validly formatted class file, it should throw
* an <code>IllegalClassFormatException</code>;
* while this has the same effect as returning null. it facilitates the
* logging or debugging of format corruptions.
* @param loader the defining loader of the class to be transformed,
* may be <code>null</code> if the bootstrap loader
* @param className the name of the class in the internal form of fully
* qualified class and interface names as defined in
* <i>The Java Virtual Machine Specification</i>.
* For example, <code>"java/util/List"</code>.
* @param classBeingRedefined if this is triggered by a redefine or retransform,
* the class being redefined or retransformed;
* if this is a class load, <code>null</code>
* @param protectionDomain the protection domain of the class being defined or redefined
* @param classfileBuffer the input byte buffer in class file format - must not be modified
* @throws IllegalClassFormatException if the input does not represent a well-formed class file
* @return a well-formed class file buffer (the result of the transform),
or <code>null</code> if no transform is performed.
* @see Instrumentation#redefineClasses
byte[]
transform( ClassLoader loader,
String className,
Class<?> classBeingRedefined,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain,
byte[] classfileBuffer)
throws IllegalClassFormatException;
package org.springframework.context.annotation.aspectj;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
* Signals the current application context to apply dependency injection to
* non-managed classes that are instantiated outside of the Spring bean factory
* (typically classes annotated with the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Configurable @Configurable}
* annotation).
* <p>Similar to functionality found in Spring's
* {@code <context:spring-configured>} XML element. Often used in conjunction with
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableLoadTimeWeaving @EnableLoadTimeWeaving}.
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableLoadTimeWeaving
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(SpringConfiguredConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableSpringConfigured {
package org.springframework.context.annotation.aspectj;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.aspectj.AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Role;
* {@code @Configuration} class that registers an {@code AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect}
* capable of performing dependency injection services for non-Spring managed objects
* annotated with @{@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Configurable
* Configurable}.
* <p>This configuration class is automatically imported when using the
* {@link EnableSpringConfigured @EnableSpringConfigured} annotation. See
* {@code @EnableSpringConfigured}'s javadoc for complete usage details.
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see EnableSpringConfigured
@Configuration
public class SpringConfiguredConfiguration {
* The bean name used for the configurer aspect.
public static final String BEAN_CONFIGURER_ASPECT_BEAN_NAME =
"org.springframework.context.config.internalBeanConfigurerAspect";
@Bean(name = BEAN_CONFIGURER_ASPECT_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect beanConfigurerAspect() {
return AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect.aspectOf();
注册了一个AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect类型的Bean
1.14 注册一个LoadTimeWeaver
在LoadTimeWeaver用于由Spring动态变换的类,因为它们被装载到Java虚拟机(JVM)。
要启用加载时编织,可以将其添加@EnableLoadTimeWeaving到其中一个 @Configuration类中,如以下示例所示:
@Configuration
@EnableLoadTimeWeaving
public class App...
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「素小暖」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/guorui_java/article/details/107379648
一、什么是Spring Boot
Spring Boot是一个快速开发框架,快速的将一些常用的第三方依赖整合(通过Maven子父亲工程的方式),简化xml配置,全部采用注解形式,内置Http服务器(Jetty和T
原文地址:http://log-cd.iteye.com/blog/562056
在Java 语言中,从织入切面的方式上来看,存在三种织入方式:编译期织入、类加载期织入和运行期织入。
1. 关于LoadTimeWeaving1.1 LTW与不同的切面织入时机AOP——面向切面编程,通过为目标类织入切面的方式,实现对目标类功能的增强。按切面被织如到目标类中的时间划分,主要有以下几种:1.运行期织入这是最常见的,比如在运行期通过为目标类生成动态代理的方式实现AOP就属于运行期织入,这也是Spring AOP中的默认实现,并且提供了两种创建动态代理的方式:JDK自带的针对接口的动态代...
最近在公司在折腾监控的事情,有用到LTW加载时期织入的代理去统一全部的监控框架使用,LTW比spring aop动态代理的好处在于不限制在spring容器内的bean类、而且对方法嵌套也同样支持(动态代理会生成额外的代理类解析this会有问题)
整体开启使用,主要有以下三步:
开启LTW在工程配置类上加上注解即可
@EnableLoadTimeWeaving(aspectjWeaving = EnableLoadTimeWeaving.AspectJWeaving.AUTODETECT)
LTW需要asp
随着Apache Spark,Scala也成了必学的语言,下面讲一下Eclipse搭建scala开发环境。网上有很多的教程,但是给的scala的地址下载的插件无法开发scala,会出现“JDT weaving is currently disabled”的问题,这是由于使用了错误的Scala地址。Java: jre1.8.0_40Eclipse: 4.4.1 Help-->Install ...
随着Apache Spark,scala也成了必学的语言,下面讲一下Eclipse搭建scala开发环境。
网上有很多的教程,但是给的scala的地址下载的插件无法开发scala,会出现“JDT weaving is currently disabled”的问题,这是由于使用了错误的Scala地址。
Java: jre1.8.0_40
Eclipse: 4.4...
LTW 原理:
程序启动时,在类加载期通过字节码编辑技术将切面织入目标类,这种方式叫做 LTW(Load Time Weaving)。
JDK5.0 新增了 java.lang.instrument 包,它包含能对 JVM 底层组件进行访问的类 。 我们可以在启动时通过 JVM 的 java agent 代理参数获取 JVM 内部组件的引用,以便在后续操作中使用 。 借助 JDK 动态代理,我们可以在 JVM 启动
@Retention(value=RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(value=LoadTimeWeavingConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableLoadTimeWeaving
Activates a Spring
LoadTimeWeaver for this app
接上一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43605444/article/details/121990016?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
15、注册 LoadTimeWeaver
Spring 使用 LoadTimeWeaver 在类加载到 Java 虚拟机 (JVM) 时对其进行动态转换。
要启用加载时织入,您可以将 @EnableLoadTimeWeaving 添加到您的 @Configuration 类之一,如以下示例所示:
@Configuration
文章目录AOP常用注解1. 用于开启注解AOP支持1.1 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy1.1.1 作用1.1.2 属性分析1.1.3 使用场景1.1.4 示例2. 用于配置切面2.1 @Aspect2.1.1 作用2.1.2 属性分析2.1.3 示例3. 用于配置切入点表达式3.1 @Pointcut3.1.1 作用3.1.2 使用场景3.1.3 属性分析3.1.4 示例4. 用于配置通知4.1 @Before4.1.1 作用4.1.2 使用场景4.1.3 属性分析4.1.4 示例4.2
LoadTimeWeaving技术还是比较偏陌生的,博主也是在源码学习中,发现了它,关于它的资料也不多。Spring 5 文档中只有这么少少一段介绍。
主要参考这位博主:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34279061/article/details/93034171
LoadTimeWeaving字面意义上看去就是加载期织入。看到织入,我们会联想到AOP,想到AOP,我们肯定会立马想到老生常谈的动态代理。其实AOP不止动态代理这么一种实现,不要因为我们用惯了动态代理就把这二
Spring is easy ... AspectJ is easy ... putting them together should be easy too, but there are quite some pitfalls. On this...
load-time weaving LTW 表示的是
在虚拟机载入字节码文件时动态植入AspectJ切面。 比动态代理效率更高开关 <context:load-time-weaver />创建AOP静态代理使用instrumentation,其实就是一个简化版的aop。
应用小案例,计算一个方法的执行时间。
1. 使用jboss的javassist动态改变字节码文件
2. 在虚拟机实例in
Aspectj implements the functionality also using the asm tool.
As it provides neat aspect grammars and is supported extensively by the community, I would like to switch to it. Better than Btrace , rig

